When an object is created, a default name based on its object typed will be given to the object. For example Form1 will be given to object/control with type Form, Text2, Text3,... will be given to Textbox object, Command1, Command2,.... will be given to command button object. You should immediately change the name property of the object to a name that describes the purpose of the control. Changing the Name property of your object with a name that describe the purpose with the object will make the code in your application easier to read and debug.
Visual Basic has several Standard Naming Convensions. Although you can assign any name you want to an object, but it is a better to adopt a naming convension and use it ocnsistently throughout your programms. Because it will make easier for others to understand your code.
Here it is a list of Standard Naming Convensions used in Visual Basic that assign to each type object:
The prefix you should use: chk
Example name: chkDrink
The prefix you should use: cbo
Example name: cboStore
The prefix you should use: cmd
Example name: cmdSelect
The prefix you should use: dat
Example name: datSales
The prefix you should use: dir
Example name: dirImage
The prefix you should use: drv
Example name: drvSource
The prefix you should use: fil
Example name: filSource
The prefix you should use: frm
Example name: frmEntry
The prefix you should use: fra
Example name: fraOption
The prefix you should use: grd
Example name: grdItem
The prefix you should use: hsb
Example name: hsbTemperature
The prefix you should use: img
Example name: imgEmployee
The prefix you should use: lbl
Example name: lblName
The prefix you should use: lin
Example name: linHorizontal
The prefix you should use: lst
Example name: lstCustomer
The prefix you should use: mnu
Example name: mnuReport
The prefix you should use: ole
Example name: oleObject2
The prefix you should use: opt
Example name: optCountry
The prefix you should use: pic
Example name: picFlower
The prefix you should use: shp
Example name: shpSquare
The prefix you should use: txt
Example name: txtName
The prefix you should use: tmr
Example name: tmrStep
The prefix you should use: vsb
Example name: vsbRate
How to Name Objects in VB6 Programming ?
Project Types in Visual Basic
A Visual Basic project is made up of the forms, code modules, ActiveX controls, and environmental settings required by an application (you can identify a Visual Basic project from it's extention name ".vbp"). The project lists all the files you need in your application.
By default Visual Basic offers you several project templates designed to support the development of different kinds of applications and components. The project templates contain the basic project objects and environment settings you need to create the type of application or component you want to build. When you begin to develop an application, first you have to decide what project template you will use.
By default you can select the following templates that available in Visual Basic:
By default Standard EXE projects contain a form, and you can use this project template to develop a stand-alone application.
You can use this project template to develop an application that reads or manipulates data from data sources.
Use ActiveX EXE and ActiveX DLL project templates to develop COM components that expose functionality to other applications. You can use an ActiveX EXE project template if your component will both expose functionality programmatically and run as a stand-alone application. You can use an ActiveX DLL if your component will only be used programatically by another application.
You can use ActiveX Control project template if you want to create a component that designed to be a user interface element in a form or a dialog box.
You can use ActiveX Document EXE and ActiveX Document DLL if you want to create a component that designed for use in a document object container, such as Internet Explorer.
You can use DHTML Application project template if you want to create a component that can be used on the client side of a Web application.
You can use IIS Aplication project template if you want to create a component that can be used on the server side of a Web application.
You can create a new Visual Basic project with below steps:
The New Project dialog box appears.
Or you can follow below steps if your Visual Basic application already open:
The New Project dialog box appears.
Common Terminology in Visual Basic
Like another programming language, Visual Basic also has some common terminology that required to be understood by the developers (programmers). Here are some common terms in Visual Basic:
Design time is any time when an application being developed in Visual Basic Development Environment
Run time is any time when an application is running.
Forms are windows that can be customized by the developer (programmer)
Controls are graphic that representation of objects
Object is a general term that used to describe forms and controls that make up a program
Properties are the characteristics of objects such as size, width, height, etc
Methods are the actions that object can perform
Events are the actions that recognized by forms or controls
.......
8 Basic Steps to Create a Program in Visual Basic
Visual Basic is one of even-driven programming. Creating an even-driven programs like Visual Basic requires different approach from that used in procedural languages. The approach may seem unusual, if you are experienced with procedural programming.
Here are 8 basic steps in creating an application with Visual Basic:
1. Create a Design Plan
2. Create the user interface
3. Set the properties of interface objects
4. Write code for events
5. Save the project
6. Test and debug the application
7. Make an executable file (by compiling it)
8. Create a setup application
How to Display Images in a Folder with VB6 Program ?
In this posting I will write a Sample of Simple VB6 program to display images in a directory of your computer. To display image in VB6 programming you can use LoadPicture statement. The format of statement is:
LoadPicture (Path\FileName)
For example:
LoadPicture ("Image01.jpg") -> display image named Image01.jpg in the current folder (the folder of image and the program is the same)
LoadPicture ("d:\MyPicture\Image02.bmp") -> display image named Image02.bmp that stored in folder MyPicture in drive d:
To make a VB6 program application like the above illustration you can follow below VB6 Programming tips.
In this case assumed that you have some images file (with extention .jpg or .bmp) that stored in directory D:\MyPicture.
Now you have to create a screen design like below image:
To create the screen design, please follow below steps:
Ok, program interface already done. Now the time to write code statements to functionate the controls, so the program can work. Dir1.Path = Drive1.Drive
File1.Path = Dir1.Path File1.Path = Dir1.Path
On Error GoTo ErrHandle
Image1.Picture = LoadPicture(File1.Path & "/" & File1.FileName)
Exit Sub
ErrHandle:
MsgBox "Invalid Image display"
Resume Next
So your Program coding will look like below listing:Private Sub Dir1_Change()
File1.Path = Dir1.Path
End SubPrivate Sub Drive1_Change()
Dir1.Path = Drive1.Drive
File1.Path = Dir1.Path
End SubPrivate Sub File1_Click()
On Error GoTo ErrHandle
Image1.Picture = LoadPicture(File1.Path & "/" & File1.FileName)
Exit Sub
ErrHandle:
MsgBox "Invalid Image display"
Resume Next
End Sub
Now the time to test your program, follow below tips:
Your program should like the illustration on the top of this posting, however the image you display depend on the image you have and select.
Visual Basic Standard Toolbar
The Standard Toolbar is one of Visual Basic Development Environment components. The Standard Toolbar contains buttons for many of the most commands used in Visual Basic.
The button such Open Project, Save Project, Start, Break, and End contain in this toolbar.
It also contains another button, such buttons to display Project Explorer, the Properties Window, the Toolbar, and other elements of Visual asic Development environment.
By default most Visual Basic Standard Toolbar are docked (attached) on the top of your screen. However you can undock it whenever you want. To undock it, click near the double bar along the left side of a toolbar, and drag away from its docked position. To dock a toolbar, drag it to another edge of the main window.
Many buttons exist in Visual Basic Standard Toolbar that make easier to edit your VB application:
Another buttons in Visual Basic Standard Toolbar:
With..End With Statement to Set Properties of Object in VB6
In the earlier posting I have written that you can set object properties in two session, at design-time and at run-time, although some object properties can be set in both run-time and design-time, other can be set just in design-time, and onother can be set just in run time.
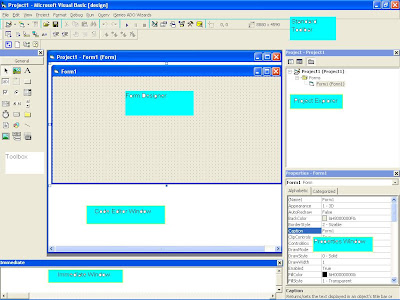
When you set object properties maybe you need to several properties at once, for example you want to set the properties of TextBox as following:
So you can do with the following coding:
Text1.Font.Bold = True
Text1.Font.Size = 24
Text1.Text = "Set Object Properties"
However to make it easier to read, and easier to understand, you can use With..End With statement to set several Object Properies.
You can use below code statement:With Text1
.Font.Bold = True
.Font.Size = 24
.Text = "Set Object Properties"
End With
Example:
Create a screen design like below image:
Note: Set property "Multiline" of Text1 and Text2 to "True".
Double-click command1 button.
Write below coding: Text1.Text = "One by one set object properties"
Text1.Font.Bold = True
Text1.Font.Size = 24
Text1.FontUnderline = True
Double-click command2 button.
Write below code statements:With Text2
.Text = "Using With..End With to set object properties"
.Font.Bold = True
.Font.Size = 24
.FontUnderline = True
End With
So your coding should like below listing:Private Sub Command1_Click()
Text1.Text = "One by one set object properties"
Text1.Font.Bold = True
Text1.Font.Size = 24
Text1.FontUnderline = True
End Sub
Private Sub Command2_Click()
With Text2
.Text = "Using With..End With to set object properties"
.Font.Bold = True
.Font.Size = 24
.FontUnderline = True
End With
End Sub
Now run our program, click command1 button, and then also click command2 button.
Your program sholud like screenshot in top of this posting.
Code Editor Window in Visual Basic
In the earlier posting I've told you that a VB Project maybe contains one or more files like form, module, and so on. One form usually contains one or more controls. However a form with it's control contained on it can't do anything without code statements (programming code) that associate with them. And a module also contains one or more statements.
A place in VB Development Environment where you can write your VB code statements (programming code) is called Visual Basic Code Editor Window. It's also known as the Code Window. A sparate Code Editor Window is displayed for each form or module in your project, making it easy to organize, view, and navigate.
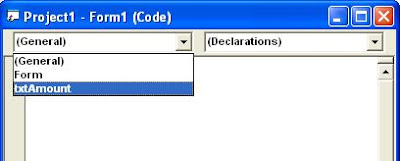
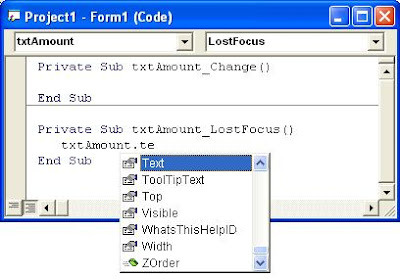
There are two drop-down lists at the top of the Code Editor Window called Object List and Procedure List.The Object list contains a list of all the Contols that exist on the form. When you selectiong a control name from the list, the Procedure list shows all the events (actions) for the control.
Using the Object and Procedure list together, can make you easy to located and edit the code you want in your VB application. The image above (on the top of posting)illustrates the Code Editor Window.
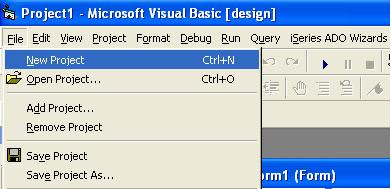
To open the Visual Basic Code Editor Window you can follow the following steps:
Tips:
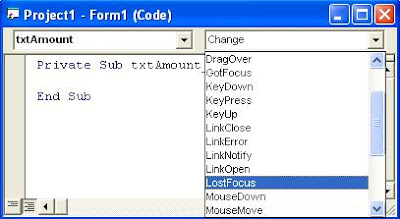
For example: You have a control called txtAmount on your form. You want to write code statements on Sub txtAmount_LostFocus(). How can you do that?
Ok, you can follow the tips below:
So, Sub txtAmount_LostFocus() appears on your screen (in the Code Editor window) and you can write your code statements you want.
Select Case...End Select - VB6 Sample Program Part 2
This posting is continuation of previous posting "Select Case...End Select - VB6 Sample Program Part 1". In the previous posting you have designed a program interface like below image, and you have saved it. Select Case Val(txtSalQty.Text) Private Sub cmdCalBonus_Click()
Now, let's writing the program coding for the above program design.
At the end, your program will look like below listing:
Case 1 To 2
txtBonus.Text = "2%"
Case 3, 4
txtBonus.Text = "3%"
Case 5 To 6
txtBonus.Text = "4.5%"
Case 7 To 8
txtBonus.Text = "6.5%"
Case 9
txtBonus.Text = "10%"
Case Else
txtBonus.Text = "15%"
End Select
txtBonusAmt.Text = Val(txtSalQty.Text) * Val(txtPriceUnit.Text) * _
Val(Left(txtBonus.Text, Len(txtBonus.Text) _
- 1)) / 100
Let's test your program to check whether it's correct or not.
Select Case Val(txtSalQty.Text)
Case 1 To 2
txtBonus.Text = "2%"
Case 3, 4
txtBonus.Text = "3%"
Case 5 To 6
txtBonus.Text = "4.5%"
Case 7 To 8
txtBonus.Text = "6.5%"
Case 9
txtBonus.Text = "10%"
Case Else
txtBonus.Text = "15%"
End Select
txtBonusAmt.Text = Val(txtSalQty.Text) * Val(txtPriceUnit.Text) * _
Val(Left(txtBonus.Text, Len(txtBonus.Text) _
- 1)) / 100
End Sub
According to the Bonus Table if Sales Quantity = 5, so the Bonus Percentage should equal to 4.5%. So the Bonus Amount = 5 X 100 X 4.5 / 100. And the result is 22.5. So your program should like below screenshot.
Now I'll explain how the program works. txtBonusAmt.Text = Val(txtSalQty.Text) * Val(txtPriceUnit.Text) * _Mybe you think that this is a complex statement. But in fact it's just a simple statement.
Val(Left(txtBonus.Text, Len(txtBonus.Text) _
- 1)) / 100
Val(txtSalQty.Text) convert text "5" into number 5
Val(txtPriceUnit.Text) convert text "100" into number 100
Because txtBonus.Text = "4.5%" (this is a text) so:
Len(txtBonus.Text) will return 4, and Len(txtBonus.Text) - 1 will return 3
Left(txtBonus.Text, Len(txtBonus.Text) - 1) equals to Left("4.5%",4-1) will return "4.5"
Then Val(Left(txtBonus.Text, Len(txtBonus.Text) - 1)) equal to Val("4.5") will return number 4.5
So the above formula will equal to:
txtBonusAmt.Text = Val("5")*Val("100")*Val(Left("4.5%",Len("4.5%")-1))/100
<=> txtBonusAmt.Text = 5 * 100 * 4.5 / 100
<=> txtBonusAmt.Text = 22.5
Select Case End Select - VB6 Sample Program Part 1
In this posting I'll write a sample of simple VB6 program that using Select Case..End Select control structure. However this program also using several VB6 functions like Val() (to convert text into number so can be calculated), Len() (to get the length of a text) and Left() (to pick up a part from the left side of a text).
The scenario of the program is as the following: Sales Quantity = 1 - 2 -> Bonus = 2%
Sales Quantity = 3 - 4 -> Bonus = 3%
Sales Quantity = 5 - 6 -> Bonus = 4.5%
Sales Quantity = 7 - 8 -> Bonus = 6.5%
Sales Quantity = 9 -> Bonus = 10%
Sales Quantity = 10 or more -> Bonus = 15%
The screen design of the program is like below screenshot.
Now, let's design the program first (create screen interface).
Look at image above, your screen design should like that.
Ok, now the time to save your work (your program) in order you can edit it next time (this program will be used in the next posting). Here it is tips to save your VB6 program:
Note: The extention .vbp and .frm will automatically given by the system.
Ok, now your program has been saved. You have 2 files in your project: prjBonus.vbp and frmCalBonus.frm and you can close your VB program. I'll continue to write the program coding in the next posting.
How to Add Controls to Form in VB6 Programming
In the previous posting I've told you that one of Visual Basic Development Environment's element is Toolbox, that contains controls. And another element is Form Design window (Form). You can place controls into your Form to build your VB application.
Now, how to place controls from Toolbox into your Form? Ok, it's just a simple way to do that. You just click, drag and drop the control you want. Or also you can double-click the icon Toolbox of the control you want.
There are two manners to place (add) controls to a form. The first manner is double-click the Toolbox icon of the control you want to add. In instance it will place the control with default size in the centre of active form.
When you adding more than one controls with this way, they will be placed on the top of each other in the center of the form. Then you can reposition/rearrange them into new place you want in the form.
The second manner, you can follow below steps:
After you add controls to your form, you can reposition them to new location in the form, and also you can resize them according to your need. That are the way how to add / place control to your Visual Basic form.
Ok, I think you get it. And I'll write another Visual Basic tips in the next posting.
If...Then...Else...End If Statement in VB6 - Sample Program 1
Visual Basic program application usually use If..Then..Else..End If statement. In this posting I would like to write a sample of simple program in VB6 which use If..Then..Else..End If statement with 2 conditions or more.
The syntax of the statement is the following:
If Condition-1 Then
Statement-1
Else
Statement-2
End If
If Condition-1 Then
Statement-1
Else
If Condition-2 Then
Statement-2
Else
If Condition-3 Then
Statement-3
Else
Statement-4
End If
End If
End If
Note: If the conditions are too much it is not effective if using If..Then..Else..End If statement, however it is better using Select Case..End Select statement.
The scenario of the program is as below:
Your program coding will look like the folling list:
Private Sub cmdRegister_Click()
'recheck data validity
If txtName.Text = "" Then
MsgBox "You must fill in the Name first"
Exit Sub
End If
If txtGender.Text = "" Then
MsgBox "You must fill in the Gender code"
Exit Sub
End If
If txtGender.Text <> "M" And txtGender.Text <> "F" Then
MsgBox "Just 'M' or 'F' for the Gender code "
Exit Sub
End If
'display greeting
lblGreeting.Caption = "Welcome " & IIf(txtGender.Text = "M", "Mr. ", "Mrs. ") & _
Trim(txtName.Text) & ". Thank you for joining our club."
End Sub
Private Sub Form_Load()
lblGender.Caption = ""
lblGreeting.Caption = ""
End Sub
Private Sub txtGender_Change()
If txtGender.Text <> "M" And txtGender.Text <> "F" Then
MsgBox "Invalid value, you should fill in 'M' or 'F'"
Else
If txtGender.Text = "M" Then
lblGender.Caption = "Male"
Else
lblGender.Caption = "Female"
End If
End If
If txtName.Text <> "" Then
cmdRegister.Enabled = True
Else
cmdRegister.Enabled = False
End If
End Sub
Private Sub txtName_Change()
If txtName.Text = "" Then
cmdRegister.Enabled = False
Else
If txtGender.Text = "" Then
cmdRegister.Enabled = False
Else
cmdRegister.Enabled = True
End If
End If
End Sub
Please look at below screen shot as your illustration:

If...Then...Else...End If Statement in VB
If..Then..Else..End If statement is one of conditional statements in Visual Basic 6 Programming. The statement format is as the following:
If Condition1 ThenStatement1 will be executed if Condition1 met (the condition1 result is true value), otherwise the Statement2 will be executed.
Statement1
Else
Statement2
End If
If Condition1 ThenIf Condition1 met, the Statement1 will be executed, if Condition2 met, the Statement2 will be executed, and so on.
Statement1
Else
If Condition2 Then
Statement2
Else
If Condition3 Then
Statement3
Else
Statement4
End If
End If
End If
Note: that Statement1, Statement2 and so on may be a single statement or a block of statements (one or more statements).
Example implementation on your program as follow:
In an examination if the student get mark more than or equal to 6 he/she pass the exam, however if his/her mark is less than 6 he/she fail.
So the program coding will be like this:
If Val(txtMark.Text) >= 6 ThenLook at below image for your illustration:
lblResult.Caption = "PASS"
Else
lblResult.Caption = "FAIL"
End If

In an examination the mark will be categorized as below conditions:
Mark = 10 is Excellent
Mark >= 9 and <10 is Very Good
Mark >= 8 and < 9 is Good
Mark < 8 is Poor
So the program coding will look like below list:
If Val(txtMark.Text) < 8 ThenLook at below image for your illustration:
lblCategory.Caption = "POOR"
Else
If Val(txtMark.Text) >= 8 And Val(txtMark.Text) < 9 Then
lblCategory.Caption = "GOOD"
Else
If Val(txtMark.Text) >= 9 And Val(txtMark.Text) < 10 Then
lblCategory.Caption = "VERY GOOD"
Else
lblCategory.Caption = "EXCELLENT"
End If
End If
End If

Project Explorer Window in Visual Basic
Project Explorer Window is one of element of Visual Basic Development Environment, that contains list of all files that build a VB application. The collection of files in a VB application called VB Project (with extention .vbp abbrefiation of Visual Basic Project). Several file types may exists in VB project, for example Form (with extention .frm), Module (with extention .bas), Designer (with extention .dsr), and so on. The sum of files in your Project depend on the size of your application, maybe some applications have many files, but others maybe have just several files.
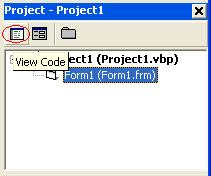
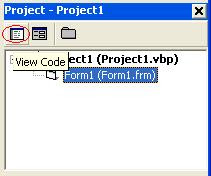
You can switch between Object and Code window by clicking Object View button and Code View button on the Project Explorer window's Toolbar. Before clicking View Object button or View Code button you must select the file first by clicking on it.
Look at below image for your illustration.
You can switch to Object window by clicking View Object button on the Project Explorer Window's toolbar. Look at below image for illustration.
You can switch to Code window by clicking View Code button on the Project Explorer Window's toolbar. Look at below image for your illustration.
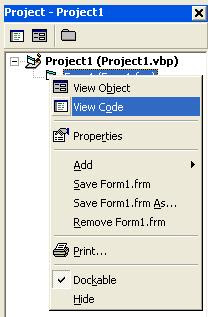
Also you can switch between Object and Code window with below VB programming tips:
A drop down menu will appear on your screen.
Look at below screen shot.
Visual Basic Properties Window
In previous posting I have written some of VB Development Environment element. One of another Visual Basic Development Environment element is Properties Window. With Visual Basic Properties window you can set the properties own to objects in your program. You can set the value of properties of object at design time (the time when the program being designed). You may find many properties of an object in Properties Window.
Properties of an object reflect the characteristic of the object (for example Width, Height, and so on). Each object in VB6 program has its own properties. Different object has different properties. For example properties of text box are Name, Alignment, Appearance, Locked, Text, etc. Properties of label are Name, Alignment, Appearance, Locked, Caption, etc. Some of Text box properties are the same as Label properties, but some are different. For example Text box has a property called Text that not owned by Label property. In opposite, Label has a property called Caption that not owned by Text box.
Each property of object has a default value, however you can change the value of property thru properties window at design time. However some of properties can be changed at run time (when the program running). Some of properties of the objects just can be changed at design time, however some just at run time, and others can be changed both at design time and run time.
Look at below screenshot for your illustration.
Stop Dreaming Start Action
Stop Dreaming Start Action is a phrase that be a key-word in a SEO contest that held by Jokosusilo.com website. Stop Dreaming Start Action is also a slogan of Jokosusilo's website, an Indonesian internet marketer. When the SEO contest starts so many Indonesian bloggers (estimated more than one thousand Indonesian bloggers) take place on the contest. The contest started on 20th June, 2009 and would finish on 15th September, 2009 at 09.00 Jakarta time. And the winners would be announced on the day. The registration would finish on 14th September, 2009 one day before the contest closed.
Stop Dreaming Start Action itself means that we don't just dream, we must stop dream, however we have to take action as soon as to reach all of our will, to reach all of our dreams, to reach our success. Because nothing will happend without action. Success won't come itself without hard working. To reach our success we have stop dream, and take action with hard working.
Everyone who health his/her body and mental must have goals, have desire. Also you and me with no exception must have desire, have dreams too. A goal would not come true by itself, unless with a real action, with hard working. You have to Stop Dreaming Start Action to achieve your goals.
You have to Stop Dreaming Start Action. For example you want to be a rich man, it is imposible you suddenly will be the rich man. It is imposible just say "bim salabim abra kadabra" and suddenly a hill of money falling down in front of you, imposible man! To be a rich man you must learn more and more, you have to work hard, and save your money, so you will be rich.
That is the mean of Stop Dreaming Start Action for me, stop your dreaming and start to take action in order all of your dreams come true. Every thing you want to achieve, you have to Stop Dreaming and Start Action as soon as. Ok, how about you... what is the meaning of Stop Dreaming Start Action? Have you done it? I hope it can be an inspiration for me, you, and all of us. Keep on Stop Dreaming Start Action.
Indonesian language:
Stop Dreaming Start Action merupakan sebuah frasa yang menjadi kata kunci dari kontes SEO yang diadakan oleh situs Jokosusilo.com. Stop Dreaming Start Action juga merupakan slogan dari situs Jokosusilo tersebut, salah satu internet marketer dari Indonesia. Ketika kontes SEO tersebut dibuka begitu banyak bloger dari Indonesia (diperkirakan lebih dari satu ribu blogger dari Indonesia) yang ikut ambil bagian dalam kontes tersebut. Kontes SEO tersebut dimulai pada tanggal 20 Juni 2009 dan akan berakhir pada tanggal 15 September 2009, pada jam 09.00 waktu Jakarta (WIB). Dan para pemenangnya akan diumumkan pada hari itu juga. Pendaftaran akan berakhir pada tanggal 14 September 2009, satu hari sebelum kontes ditutup.
Stop Dreaming Start Action itu sendiri memiliki arti kita jangan hanya menjadi orang yang suka bermimpi, kita harus berhenti dari bermimpi, namun sebaliknya kita harus segera melakukan suatu tindakan untuk meraih semua keinginan kita, untuk mencapai semua impian kita, untuk mencapai kesuksesan kita. Karena tiada hal akan terjadi tanpa suatu tindakan. Kesuksesan tidak akan datang dengan sendirinya tanpa dibarengi dengan kerja keras. Untuk mencapai kesuksesan kita harus berhenti dari menjadi seorang yang hanya bermimpi, dan harus melakukan suatu tindakan dengan bekerja keras sekuat tenaga.
Setiap orang yang memiliki kesehatan jasmani dan kesehatan rohani sudah pasti mempunyai cita - cita, mempunyai keinginan - keinginan. Begitu juga anda dan saya tanpa kecuali pasti mempunyai keinginan - keinginan, mempunyai impian - impian. Suatu cita - cita tidak akan tercapai dengan sendirinya, kecuali dengan suatu usaha yang sungguh - sungguh, dengan bekerja keras. Anda harus Stop Dreaming Start Action untuk mencapai cita - cita anda.
Anda harus Stop Dreaming Start Action. Misalnya anda ingin menjadi seorang yang kaya raya, maka tidak mungkin dengan serta merta anda menjadi kaya raya. Tidak mungkin hanya dengan mengatakan "bim salabim abra kadabra" dan kemudian segunung uang tiba - tiba "GEDUBRAK" jatuh di hadapan anda, itu tidak mungkin dong! Untuk menjadi kaya - raya anda harus belajar dengan sungguh - sungguh dan bekerja keras dan harus rajin menabung, maka lama - lama anda akan bisa menjadi kaya.
Begitulah dari sudut pandang saya bahwa Stop Dreaming Start Action memiliki arti Berhentilah dari menjadi seorang yang suka bermimpi dan mulailah berusaha agar mimpi - mimpi kita dapat menjadi kenyataan dengan cara bekerja keras. Terhadap segala sesuatu yang ingin anda capai, anda harus sesegera mungkin Stop Dreaming dan Mulai Melakukan Action. Ok, bagaimana menurut anda... apa arti dari Stop Dreaming Start Action? Apakah anda telah melakukannya? Saya berharap hal ini dapat menjadi inspirasi bagi saya, anda, dan kita semua. Tetaplah melakukan Stop Dreaming Start Action untuk menggapai cita-cita anda.
Form Designer Window in Visual Basic
In the earlier posting I have written about Visual Basic Development Environment wich has several elements. One of its element is Toolbox that contains object and controls, and I also already written in the next posting. Now I'll write another component, it is Visual Basic Form Designer Window. Ok, let's go on.
Likes another visual programming software, Visual Basic also has Form Designer Window. When you open your Visual Basic software, and select a type of project type, it will create a Form. By default a new Visual Basic Form contains minimum parts of it. It contains Form area where you can place controls you want, Title Bar where you can place title of your Form, Minimize button, Maximize button, and close button.
Look at below picture for your illustration.
Now what's the Form Designer Window used for ?
Applications that develop with Visual Basic Programming Language usually contain one Form or more. You can design your form in a Form Designer Window by adding controls you need, arrange and set them up to make your program interface. So you can make your user friendly program. You can setup your controls at design time in this form.
Temperature Conversion with Multiple Base in VB6
In the earlier posting you have learnt several simple VB programming tips how to convert temperature with basis Celcius, Fahrenheit, Rheamur and Kelvin. In this posting you will learn how to make a simple application to convert temperature with multiple basis with VB6 programming. You can select the temperature basis when the program's running.
The scenario of this simple application is as follow:
Now, how to built your simple application? Let's go on to the simple VB programming tips.
First, you have to create a screen design likes below image:
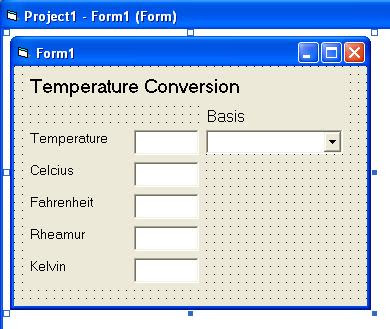
How to create the screen design? Follow step by step of below instructions:
Ok, the screen design already finished. Now, what's the program coding like?
Here it is the program coding. Follow the next simple VB programming tips.
'to add items in combo box
cboBasis.AddItem "Celcius"
cboBasis.AddItem "Fahrenheit"
cboBasis.AddItem "Rheamur"
cboBasis.AddItem "Kelvin"
'call procedure ConvPro
ConvPro
'call procedure ConvPro
ConvPro
Private Sub ConvPro()
If TxtTemp.Text = "" Then
'clear the text of text boxes
TxtCel.Text = ""
TxtFah.Text = ""
TxtRhe.Text = ""
TxtKel.Text = ""
Exit Sub
End If
'if Basis is blank then fill in with "Celcius" as default
If cboBasis.Text = "" Then
cboBasis.Text = "Celcius"
End If
Select Case cboBasis.Text
Case "Celcius"
GoTo ConvCel
Case "Fahrenheit"
GoTo ConvFah
Case "Rheamur"
GoTo ConvRhe
Case Else
GoTo ConvKel
End Select
'conversion for celcius basis
ConvCel:
TxtCel.Text = Val(TxtTemp.Text)
TxtFah.Text = Val(TxtTemp.Text) * 1.8 + 32
TxtRhe.Text = Val(TxtTemp.Text) * 0.8
TxtKel.Text = Val(TxtTemp.Text) + 273.15
Exit Sub
'conversion for fahrenheit basis
ConvFah:
TxtFah.Text = Val(TxtTemp.Text)
TxtCel.Text = (Val(TxtTemp.Text) - 32) / 1.8
TxtRhe.Text = ((Val(TxtTemp.Text) - 32) / 1.8) * 0.8
TxtKel.Text = ((Val(TxtTemp.Text) - 32) / 1.8) + 273.15
Exit Sub
'conversion for rheamur basis
ConvRhe:
TxtRhe.Text = Val(TxtTemp.Text)
TxtCel.Text = Val(TxtTemp.Text) / 0.8
TxtFah.Text = ((Val(TxtTemp.Text) / 0.8) * 1.8) + 32
TxtKel.Text = (Val(TxtTemp.Text) / 0.8) + 273.15
Exit Sub
'conversion for kelvin basis
ConvKel:
TxtKel.Text = Val(TxtTemp.Text)
TxtCel.Text = Val(TxtTemp.Text) - 273.15
TxtRhe.Text = (Val(TxtTemp.Text) - 273.15) * 0.8
TxtFah.Text = ((Val(TxtTemp.Text) - 273.15) * 1.8) + 32
End Sub
So your program will look like below listing:
Private Sub ConvPro()
If TxtTemp.Text = "" Then
'clear text of text boxex
TxtCel.Text = ""
TxtFah.Text = ""
TxtRhe.Text = ""
TxtKel.Text = ""
Exit Sub
End If
'if Basis is blank then fill in with "Celcius"
If cboBasis.Text = "" Then
cboBasis.Text = "Celcius"
End If
Select Case cboBasis.Text
Case "Celcius"
GoTo ConvCel
Case "Fahrenheit"
GoTo ConvFah
Case "Rheamur"
GoTo ConvRhe
Case Else
GoTo ConvKel
End Select
'conversion for celcius basis
ConvCel:
TxtCel.Text = Val(TxtTemp.Text)
TxtFah.Text = Val(TxtTemp.Text) * 1.8 + 32
TxtRhe.Text = Val(TxtTemp.Text) * 0.8
TxtKel.Text = Val(TxtTemp.Text) + 273.15
Exit Sub
'conversion for fahrenheit basis
ConvFah:
TxtFah.Text = Val(TxtTemp.Text)
TxtCel.Text = (Val(TxtTemp.Text) - 32) / 1.8
TxtRhe.Text = ((Val(TxtTemp.Text) - 32) / 1.8) * 0.8
TxtKel.Text = ((Val(TxtTemp.Text) - 32) / 1.8) + 273.15
Exit Sub
'conversion for rheamur basis
ConvRhe:
TxtRhe.Text = Val(TxtTemp.Text)
TxtCel.Text = Val(TxtTemp.Text) / 0.8
TxtFah.Text = ((Val(TxtTemp.Text) / 0.8) * 1.8) + 32
TxtKel.Text = (Val(TxtTemp.Text) / 0.8) + 273.15
Exit Sub
'conversion for kelvin basis
ConvKel:
TxtKel.Text = Val(TxtTemp.Text)
TxtCel.Text = Val(TxtTemp.Text) - 273.15
TxtRhe.Text = (Val(TxtTemp.Text) - 273.15) * 0.8
TxtFah.Text = ((Val(TxtTemp.Text) - 273.15) * 1.8) + 32
End Sub
Private Sub cboBasis_Click()
'call procedure ConvPro
ConvPro
End Sub
Private Sub Form_Load()
'to add items in combo box
cboBasis.AddItem "Celcius"
cboBasis.AddItem "Fahrenheit"
cboBasis.AddItem "Rheamur"
cboBasis.AddItem "Kelvin"
End Sub
Private Sub TxtTemp_Change()
'call procedure ConvPro
ConvPro
End Sub
What happen? The conversion should automatically occurs, so the results appear on the each text box. Look at below image for your illustration. Your program should look like it.

Visual Basic Toolbox
The Visual Baisc Toolbox contains the objects and controls that you can add to forms to create the user interface of your VB applications. In the next time I'll explain how to place the controls from toolbox into Visual Basic Screen Design area in Screen Design Window. This toolbox is the General Toolbox. There is also a Datareport Toolbox that contains objects and controls that you can use for your Datareport design.
You can add additional controls to the Toolbox by using Components command on the Project menu. Also you can right-click anywhere in the Toolbox and select Component from the pop up menu.
Look at below screen shot for your illustration.
Below is a simple VB programming tips how to add controls to the Toolbox. Keep on reading the tips.
A Components window will appear on your screen.
What's Visual Basic Development Environment ?
When you start your Visual Basic and select a project type, a graphical development environment appears on your screen. In this Visual Basic Development Environment you can develop your Visual Basic applications. You can design your Visual Basic program interface and write your program code. And also you can run your Visual Basic Program for testing and compile them.
Development Environment in Visual Basic has several elements, such as:
Each elements has specific funcions, however they all make easy to develop your VB applications.
Look at below image for your illustration.
In the next posting I will explain each above component, what they used for, and how to use them.
How to Save Your VB Program?
In the pervious posting I have written a tips how to start using VB6 programming software. When you open your VB program software a project (Project1) and a form (Form1) automatically created. These are your VB programs. However at the moment they just saved in the memory of your computer, so if suddenly your computer is off the programm will loose from your computer memory. You can't use your programm you have created next time before you save them into your harddisk. In order you can use your programm next time you must save your programm into your harddisk. After you save your programs into your harddisk you can reopen, reuse and edit your programs whenever you want.
Now, how to save your VB program into your harddisk? Keep on reading below simple VB programming tips.
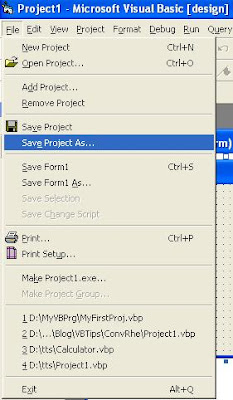
It's just a simple way to do. It's a good thing before you save your programs, you have to define first "what your VB project name", "what your VB form name", and "where your program will be saved in(which folder)".
For example you will save your program in a folder called D:\MyVBPrg, and your project name is MyFirstProj, and your form is MyFirstForm. Now, lets do the following instructions to save your VB program:
Look at below screen shot.
Then a Save File As window will appear on your screen.
Then a Save Project As window will appears on your screen
Now your program's been saved already in folder D:\MyVBPrg with file name MyFirstProj.vbp (a VB Project file) and MyFirstForm.frm (a VB Form file). The extention .vbp and .frm are automatically given by Visual Basic software. Look at below image for your illustration.
Have you any comment? Please write down your commant in below comment box.
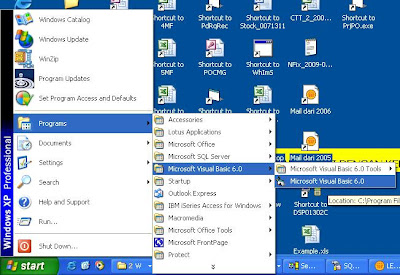
How to Start Using VB 6 Programming ?
You can find out the right order of the postings in a posting with title. "Contents". This posting for you who using VB6 programming software for the first time.
Before you start using VB6 programming software, you must have a VB6 software installed in your computer with Operating System Windows family. To start using it you can follow below instructions.
Please look at below image for your illustration:
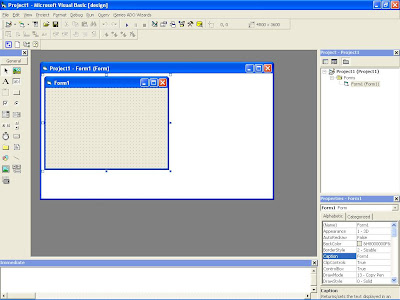
A VB project (Project1) and a Form (Form1) are automatically created. Now you are ready to design and create your VB6 program. Look at below picture for illustration.
What do you think? Please write down in below comment box.
How to Convert Degree from Kelvin to Another in VB 6 Programming?
In this posting I will write a simple VB programming tips "How to convert degree from Kelvin into Celcius, Fahrenheit and Rheamur" using VB6 programming. Let's go on to the simple tips. Your program will look like below coding:
We have three previous conversion formulas (Celcius base) as follow in the erlier postings:
Fahrenheit = ( Celcius X 1.8 ) + 32
Rheamur = Celcius X 0.8
Kelvin = Celcius + 273.15
From previous formulas we got another three formulas with Kelvin degree basis as the following:
Celcius = Kelvin - 273.15
Fahrenheit = ( ( Kelvin - 273.15 ) X 1.8 ) + 32
Rheamur = ( Kelvin - 273.15 ) X 0.8
Let's implement these formulas in a simple VB6 programming.
First you should create a screen design like below image (just a simple screen design):
How to create this screen design? Follow below instructions for the tips.
'conversion process
txtCelcius.Text = Val(txtKelvin.Text) - 273.15
txtRheamur.Text = (Val(txtKelvin.Text) - 273.15) * 0.8
txtFahrenheit.Text = ((Val(txtKelvin.Text) - 273.15) * 1.8) + 32
Private Sub cmdConvert_Click()
'conversion process
txtCelcius.Text = Val(txtKelvin.Text) - 273.15
txtRheamur.Text = (Val(txtKelvin.Text) - 273.15) * 0.8
txtFahrenheit.Text = ((Val(txtKelvin.Text) - 273.15) * 1.8) + 32
End Sub
Now the time to test your program.
Look at below image, and your result should look like it.
What about your idea? Any comment?
Labels
- Stop Dreaming Start Action (1)
- Table of Contents (1)
- VB6 Programming (36)
- VB6 Sample Program (16)